What we cover in this article
This blog explains the power of business analytics dashboards, which offer real-time insights by consolidating key metrics across various business functions. Benefits include improved decision-making, early problem detection, and fostering a data-driven culture. Different dashboards, such as sales, financial, and marketing, provide tailored insights to help optimize performance and efficiency.
Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Business Analytics Dashboard?
- Benefits of Using a Business Analytics Dashboard
- Types and Examples of Analytics Dashboards for Businesses
- Business Analytics Dashboard Best Practices
- Next Steps: Creating or Accessing a Business Dashboard Solution
Introduction
Imagine having a crystal-clear, real-time view of every important metric in your business right at your fingertips. No more waiting for monthly reports or sieving through outdated spreadsheets. Just instant access to insights about your business operations. That’s exactly what business analytics dashboards offer.
A recent Wavestone survey reveals that 87% of business leaders consider investments in data and analytics a top organizational priority. This further underscores the importance of streamlining your business data.
Business analytics dashboards transform your raw business data into actionable insights you need to assess your status and determine ways to drive your company forward. In this Minimal Dashboard article, we’ll explain what business analytics dashboards are, how they work, the different types, and how you can get the most out of them.
What is a Business Analytics Dashboard?
A business dashboard is a powerful tool designed to provide a visual representation of your company’s key metrics and data points in one easily accessible place. It consolidates data from multiple sources into a single interface and simplifies them, enabling you to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
Instead of manually compiling spreadsheets and presentations, modern business analytics dashboards can access, analyze, display, and share data via web-based dashboards. Think of it as the command center for your business, offering real-time insights into various aspects of your operations.
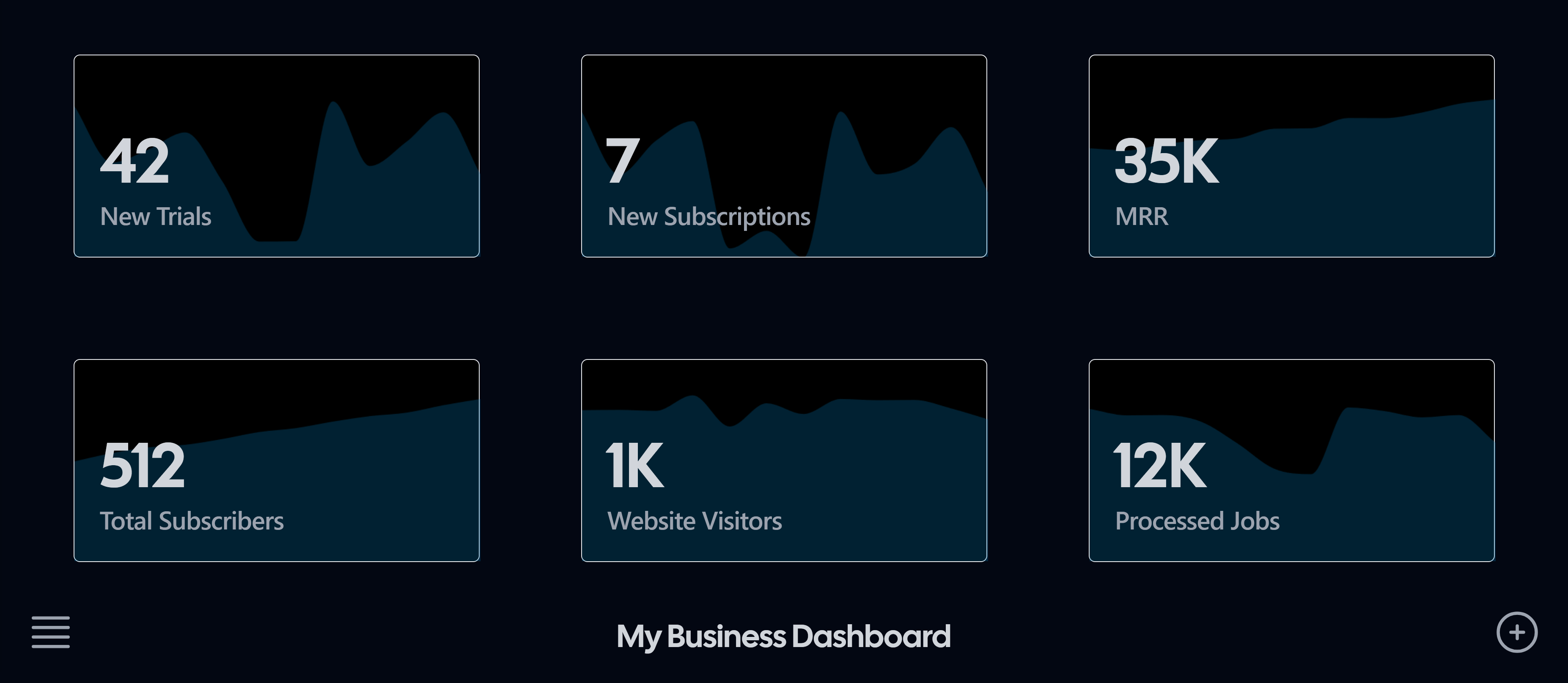
Some of the data you find in a business analytics dashboard include:
- Sales Metrics: This includes total sales, sales growth, sales by region or product, and conversion rates.
- Marketing Metrics: These metrics cover website traffic, lead generation, campaign performance, and customer acquisition costs.
- Financial Metrics: Key financial metrics include revenue, profit margins, expenses, and cash flow.
- Operational Metrics: Operational data might include inventory levels, supply chain efficiency, production rates, and quality control metrics.
- Customer Metrics: Important customer-related metrics are customer satisfaction scores, net promoter score (NPS), customer retention rates, and customer lifetime value (CLV).
Whether you’re tracking sales, monitoring staff performance, or keeping an eye on profitability, a business dashboard helps you stay on top of what matters most.
Benefits of Using a Business Analytics Dashboard
Here are some of the reasons your business should adopt an analytics dashboard:
Access Business Information At-a-Glance
Business analytics dashboards help you quickly access key data to make informed decisions. By visualizing trends and patterns, you can better allocate resources and make necessary changes. For example, a sales dashboard can show daily sales performance, helping managers identify which products are performing well and which need attention.
Inform Decision-Making and Strategic Planning
A business analytics dashboard empowers you to make data-driven decisions. By presenting key metrics in an easy-to-understand format, it allows you to spot trends and patterns quickly. For example, a marketing manager can use a dashboard to detect that social media ads are outperforming email marketing and then allocate more resources to social media campaigns to improve the marketing ROI.
Create a Data-Driven Culture
Implementing a business analytics dashboard across your organization promotes a data-driven culture. When everyone has access to relevant metrics, it encourages employees at all levels to base their decisions on data rather than gut feeling. This approach aligns individual efforts with overall business objectives and improves accountability.
Early Problem Detection and Issue Resolution
Business dashboards act as an early warning system, alerting you to potential problems before they escalate. By setting up thresholds and alerts, you can quickly identify and address issues. For instance, a manufacturing company can detect an increase in defect rates on its dashboard by tracking production efficiency. This allows the team to investigate early and fix the problem before it leads to costly recalls.
Timely Access to Information for Everyone
Dashboards provide easy access to key information for all stakeholders, not just data analysts. Marketing managers, finance personnel, and even customers can benefit from centralized dashboards. For instance, a marketing dashboard can display campaign performance metrics, enabling marketers to adjust strategies in real time.
Time-Saving and Efficiency Boost
By automating data collection and visualization, business analytics dashboards save considerable time that would otherwise be spent on manual reporting. This efficiency allows you and your team to focus on analyzing insights and taking action rather than gathering and formatting data.
Types and Examples of Analytics Dashboards for Businesses
There are different types of business analytics dashboards, each tailored to the needs and objectives of the department using them.
Sales Dashboards
Sales dashboards focus on tracking the performance of a company’s sales activities. Sales managers and teams use these dashboards to monitor sales targets, track conversion rates, and analyze sales pipeline health. They help in identifying high-performing sales strategies and areas needing improvement.
Key metrics often tracked in sales dashboards include:
- Sales Revenue: Total income generated from sales. Indicates overall sales performance.
- Sales Growth: Measures the increase in sales over a specific period. Reflects business expansion and market penetration.
- Conversion Rate: Percentage of leads that turn into sales. Assesses the effectiveness of sales strategies.
- Sales Pipeline: Tracks potential sales opportunities at different stages. Helps manage and forecast future sales.
- Average Order Value: The average amount spent per transaction. Indicates the effectiveness of upselling and cross-selling strategies.
For example, a software company could use a sales dashboard to track its subscription sales and renewals. By monitoring sales amounts by product category (e.g., different software packages), region, and sales channel (e.g., direct sales, online sales), the company can identify which products and regions are performing well and which need more attention.
Suppose the dashboard shows that sales in a particular region are below target. In that case, the sales team can allocate more resources to that region, such as increasing marketing efforts or providing additional training to the sales team.
) Sales Dashboards](/images/blog/business-analytics-dashboards-heres-what-you-need-to-know/image6.png)
Financial Dashboards
Financial dashboards provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health. This enables CFOs and finance teams to monitor key financial metrics in real-time. These dashboards help in making informed decisions about budgeting, forecasting, and resource allocation.
Key metrics often tracked in financial dashboards include:
- Revenue: Total income generated from sales before deducting expenses.
- Gross Profit Margin: Percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold.
- Operating Expenses: Costs associated with running the business, excluding direct production costs.
- Net Profit: Revenue minus all expenses, including taxes and interest.
- Cash Flow: Movement of money in and out of the business.
- Accounts Receivable/Payable: Money owed to the company by customers or owed by the company to suppliers.
For example, a retail store could use the financial dashboard below to track metrics such as total sales revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net profit margin. If the store notices a decline in sales during weekdays, it can introduce weekday promotions or discounts to boost sales.
The store can also compare current sales figures with historical data to identify seasonal trends and plan inventory accordingly.
) Financial Dashboard](/images/blog/business-analytics-dashboards-heres-what-you-need-to-know/image5.png)
Marketing Dashboards
The next dashboard on the list is the one for marketers. Marketing dashboards aggregate data from various marketing channels to provide insights into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. These dashboards help the marketing team to track campaign performance, customer engagement, and ROI. Based on the insights obtained, they can refine marketing strategies and allocate resources more effectively.
Some of the key metrics a marketing dashboard tracks include:
- Website Traffic: Measures the number of visitors to the website. Indicates the reach and visibility of marketing efforts.
- Lead Generation: Tracks the number of potential customers identified. Reflects the effectiveness of lead acquisition strategies.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that take a desired action, such as signing up or purchasing. Shows the success of marketing campaigns.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): The cost associated with acquiring a new customer. Helps in evaluating the efficiency of marketing spend.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising
- Engagement Rate: Level of audience interaction with content across various platforms
Suppose a SaaS company offering a project management tool uses a marketing dashboard to track its digital marketing campaigns. In that case, it can monitor metrics like website traffic, conversion rates, and customer acquisition costs from various channels, such as social media, referrals, email marketing, and paid ads.
So, if the data from the dashboard shows that email marketing is generating more qualified leads compared to referrals, the company can allocate more budget towards email campaigns.
) An example of a Marketing Dashboard (Source: HubSpot)](/images/blog/business-analytics-dashboards-heres-what-you-need-to-know/image3.png)
Human Resource (HR) Dashboards
HR dashboards monitor and manage various human resources metrics. These dashboards provide insights into employee performance, turnover rates, and overall workforce productivity. Aggregating and analyzing this data helps HR managers to keep the workforce performing optimally. It also ensures that the company is meeting its talent management goals.
An HR dashboard can track the following metrics:
- Employee Turnover Rate: Percentage of employees leaving the organization over a period. Indicates employee retention and satisfaction.
- Time to Hire: The average time taken to fill a vacancy. Reflects the efficiency of the recruitment process.
- Employee Satisfaction: Measures overall job satisfaction among employees. Helps in identifying areas for improving workplace culture.
- Absenteeism Rate: Tracks the frequency of employee absences. Indicates potential issues with employee engagement or health.
- Training and Development: Monitors the effectiveness of employee training programs. Ensures workforce skill development aligns with company goals.
Large corporations can use an HR dashboard to monitor key metrics such as employee turnover, average time to hire, and employee satisfaction scores. If the dashboard indicates an increase in employee turnover in a particular department over a specific period, HR can investigate further to understand the underlying issues.
Similarly, if the data shows that employees are leaving because of salary, HR can streamline the remuneration process to ensure employees are adequately compensated.
) An example of an HR Dashboard (Source: Tableau)](/images/blog/business-analytics-dashboards-heres-what-you-need-to-know/image2.png)
Customer Support Dashboards
Customer support dashboards help support teams monitor and improve the quality of customer service. These dashboards provide real-time insights into support ticket volumes, response times, customer satisfaction levels, and agent performance.
Key metrics often tracked in customer support dashboards include:
- First Response Time: Average time taken to respond to a customer inquiry initially.
- Average Handle Time: Average duration of a support interaction.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Measure of how satisfied customers are with the support they receive.
- Ticket Volume: Number of support tickets received over a given period.
- Resolution Rate: Percentage of tickets resolved within a specified timeframe.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measure of customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend the company.
For example, a telecommunications company might use a customer support dashboard to track the volume of support tickets across different channels (phone, email, chat), average resolution times, and customer satisfaction scores.
If the dashboard shows a spike in ticket volume and a drop in satisfaction scores, the support team can quickly allocate more resources or identify and address the root cause of the increased complaints.
) An example of a Customer Support Dashboard (Source: Freshdesk)](/images/blog/business-analytics-dashboards-heres-what-you-need-to-know/image1.png)
Operational Dashboards
Operational dashboards monitor the day-to-day operations of a business, providing real-time data on various processes associated with efficiency and productivity. Managers can leverage this information to assess operations, identify bottlenecks, and make quick decisions to improve efficiency.
An operational dashboard can track metrics like:
- Production Output: The number of units produced in a given period. Reflects the efficiency of the production process.
- Machine Downtime: The amount of time machinery is not operational. Indicates potential issues with equipment maintenance.
- Quality Control Pass Rate: The percentage of products that pass quality inspections. Reflects the effectiveness of quality control processes.
- Inventory Levels: Tracks the amount of raw materials and finished goods on hand. Helps in managing supply chain and production planning.
- Operational Cost: Measures the total cost of running operations. Helps in identifying areas for cost reduction and efficiency improvement.
A warehouse operations company may use an operational dashboard to track key metrics such as inventory levels, order fulfillment times, and picking accuracy rates. This helps the operations manager maintain high levels of efficiency and accuracy in warehouse operations.
For example, if the inventory for a high-demand product is running low, the operations manager can quickly reorder stock to avoid stockouts and ensure continuous supply. Also, by monitoring inventory turnover rates, the manager can identify slow-moving items and make decisions to clear out excess stock.
)
An example of a Customer Support Dashboard (Source: SlideTeam)](/images/blog/business-analytics-dashboards-heres-what-you-need-to-know/image4.png)
Business Analytics Dashboard Best Practices
Here are some best practices to get the most out of your business analytics dashboards:
- Define Clear Objectives: Start by identifying the specific goals and objectives of your dashboard. Knowing what you want to achieve helps in selecting the right metrics and designing an effective dashboard.
- Know Your Audience: Understand who will be using the dashboard and tailor it to their needs. Different stakeholders may require different views and levels of detail, so customize accordingly.
- Keep It Simple: Avoid clutter by focusing on the most important metrics. A clean, straightforward design makes it easier for users to interpret the data and take action.
- Use Appropriate Visualizations: Choose the right type of chart or graph for the data you are presenting. For example, use line charts for trends over time and bar charts for comparisons.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Regularly update your data sources to ensure the information displayed is accurate and up-to-date. Inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making.
- Provide Context: Include context for the data, such as benchmarks or historical comparisons. This helps users understand the significance of the metrics and make informed decisions.
- Make It Interactive: Allow users to interact with the dashboard by filtering data, drilling down into details, and customizing their views. This enhances user engagement and insight discovery.
- Optimize for Performance: Ensure your dashboard loads quickly and performs well, even with large datasets. Slow performance can frustrate users and reduce the dashboard’s effectiveness.
- Design for Mobile: Consider how your dashboard will be viewed on different devices, including smartphones and tablets. A responsive design ensures accessibility and usability across all platforms.
- Regularly Review and Update: Your dashboard should not be set in stone. Regularly review its effectiveness and make updates based on changing business needs or user feedback.
Next Steps: Creating or Accessing a Business Dashboard Solution
Now that you’ve seen the power of business analytics dashboards, it’s time to take action. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, implementing a dashboard can transform how you make decisions and drive growth.
At Minimal Dashboard, we help businesses set up intuitive and simple dashboards that track all their key metrics at a glance. The goal is to help you stay informed, uncover trends, and assess the impact of your business decisions.
Sign up for free today and see Minimal Dashboard in action.
